High-energy Gamma Ray Burst Could Re-shape Astrophysics Theories, SLAC and Stanford Scientists Say
SLAC and Stanford physicists played a key role in monitoring and analyzing the brightest gamma ray burst ever measured, and suggest that its never-before-seen features could call for a rewrite of current theories.
By Bjorn Carey
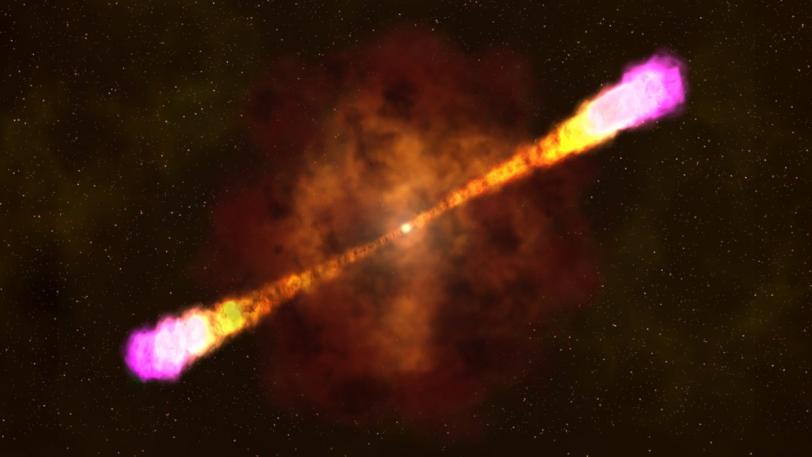
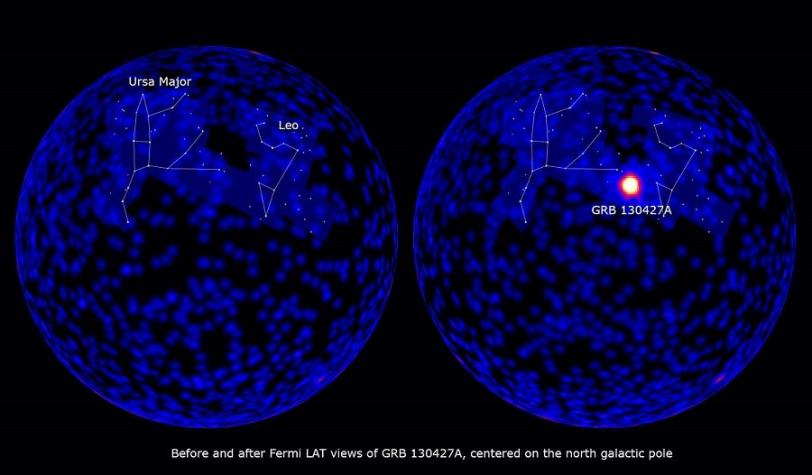
This past April, an incredibly bright flash of light burst from near the constellation Leo. Originating billions of light years away, this explosion of light, called a gamma ray burst, has now been confirmed as the brightest gamma ray burst ever observed.
Astronomers around the world were able to view the blast in unprecedented detail and observe several aspects of the event for the first time ever. The data could lead to a rewrite of standard theories of how gamma ray bursts work.
The blast, named GRB 130427A, was observed by several space- and ground-based telescopes, and the data was analyzed by dozens of astronomers around the world. The Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope was the first to detect the event, and it quickly began monitoring the flood of radiation using its Large Area Telescope (LAT), whose principal investigator is Peter Michelson, a physics professor at Stanford and the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory. Michelson leads the international collaboration that built and operates the LAT.
Fermi's quick action, allowing the LAT to record nearly the entire event, yielded incredible data that revealed previously unknown aspects of the mechanisms involved in a gamma ray burst.
The findings are reported in a series of papers published by the journal Science at the Science Express website on Nov. 21, including one by the Fermi-LAT collaboration.
A special cosmic event
Several features of GRB 130427A combined to make it of particular interest to astronomers.
First, its light traveled 3.6 billion years before arriving at Earth, about one-third of the travel time for light from typical bursts. The record-setting 20 hours that the LAT observed gamma rays was longer than any other observed GRB. And, in addition to being the brightest GRB ever witnessed, it was also one of the most energetic.
"When that happens, we start seeing features that we were not able to observe before," said Nicola Omodei, a research associate at Stanford's Hansen Experimental Physics Laboratory who led LAT data analysis for one of the Science papers. "Especially because it was very bright, you can uncover features that were not predicted by the standard models."
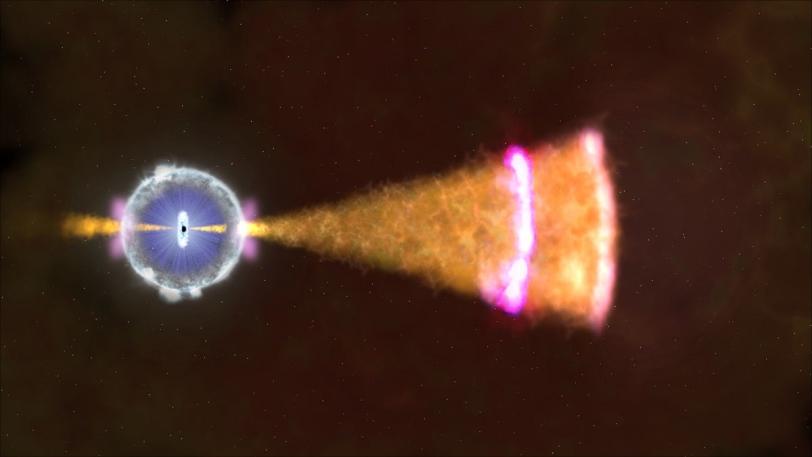
The leading theory explaining long gamma ray bursts such as GRB 130427A posits that they are created during the most energetic explosions in the cosmos, which occur when a very massive star collapses on itself.
These explosions erupt a jet of elementary particles traveling at close to the speed of light. Within the jet, pressure, temperature and density are not uniform, creating internal shock waves that move inward and outward as faster regions within the jet collide with slower ones.
As the jet travels outward, it collides with the interstellar medium to create additional shock waves, called "external shocks." Although details are not well understood, particles are accelerated at the shock front and, at the same time, interact with the surrounding electromagnetic fields. This causes particles to lose part of their energy emitting photons, through a process known as synchrotron radiation.
The balance between the gain in energy from acceleration by the shock and the loss of energy due to synchrotron radiation dictates the maximum energy of the photons that can be emitted by such a system. The highest energy photons among these are classified as gamma rays and are detected by the LAT.
The observations of GRB 130427A, however, didn't quite match energy levels predicted by these models.
An unexpected observation
For instance, the telescopes detected more photons, and more high-energy gamma rays, than theoretical models would predict for a burst of this magnitude. In particular, a few of these high-energy events are so energetic that they cannot be produced via existing models of synchrotron radiation from shock-accelerated particles.
Additionally, the prevailing thought was that the brightest flashes were driven by the explosion's internal shock waves, but the evidence indicates that these photons were created externally.
"It's like having a blanket that's too short. You pull it up to your chin and uncover your toes," Omodei said. "With our standard model, if you try to explain the pulse, you will fail to explain the energy."
The new observations don't rule out the existing model, but researchers will need to either amend portions of it or adopt a new theory altogether to account for these characteristics, said Giacomo Vianello, a postdoctoral scholar in Michelson's group and a co-author who performed LAT data analysis and interpretation on three of the Science papers.
The microphysics of how particles are accelerated involves a certain amount of well-thought assumptions, and these assumptions therefore get built into the theoretical models used to predict the behavior of cosmic events. The assumptions are necessary in part because these events cannot be recreated in laboratory settings, he said, which highlights the critical role that observations play in the fine-tuning of fundamental physics theories.
"The really cool thing about this GRB is that because the exploding matter was traveling at the speed of light, we were able to observe relativistic shocks," Vianello said. "We cannot make a relativistic shock in the lab, so we really don't know what happens in it, and this is one of the main unknown assumptions in the model. These observations challenge the models and can lead us to a better understanding of physics."
For more information, see NASA's press release.
Bjorn Carey is a science writer with the Stanford News Service.
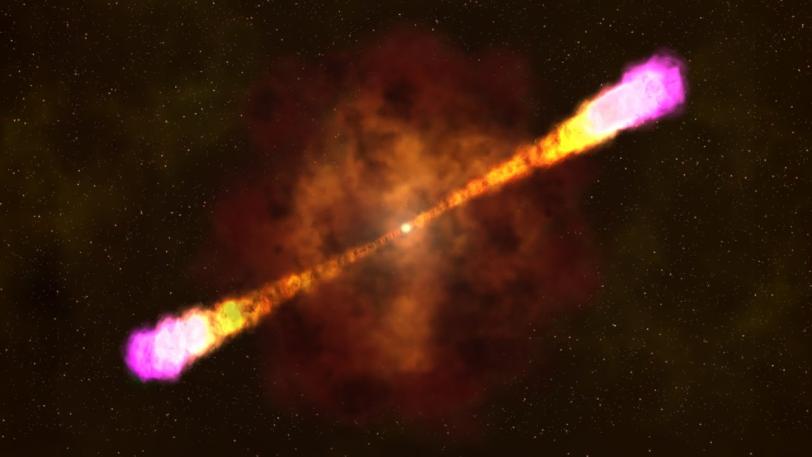

Overview Animation of Gamma-ray Burst